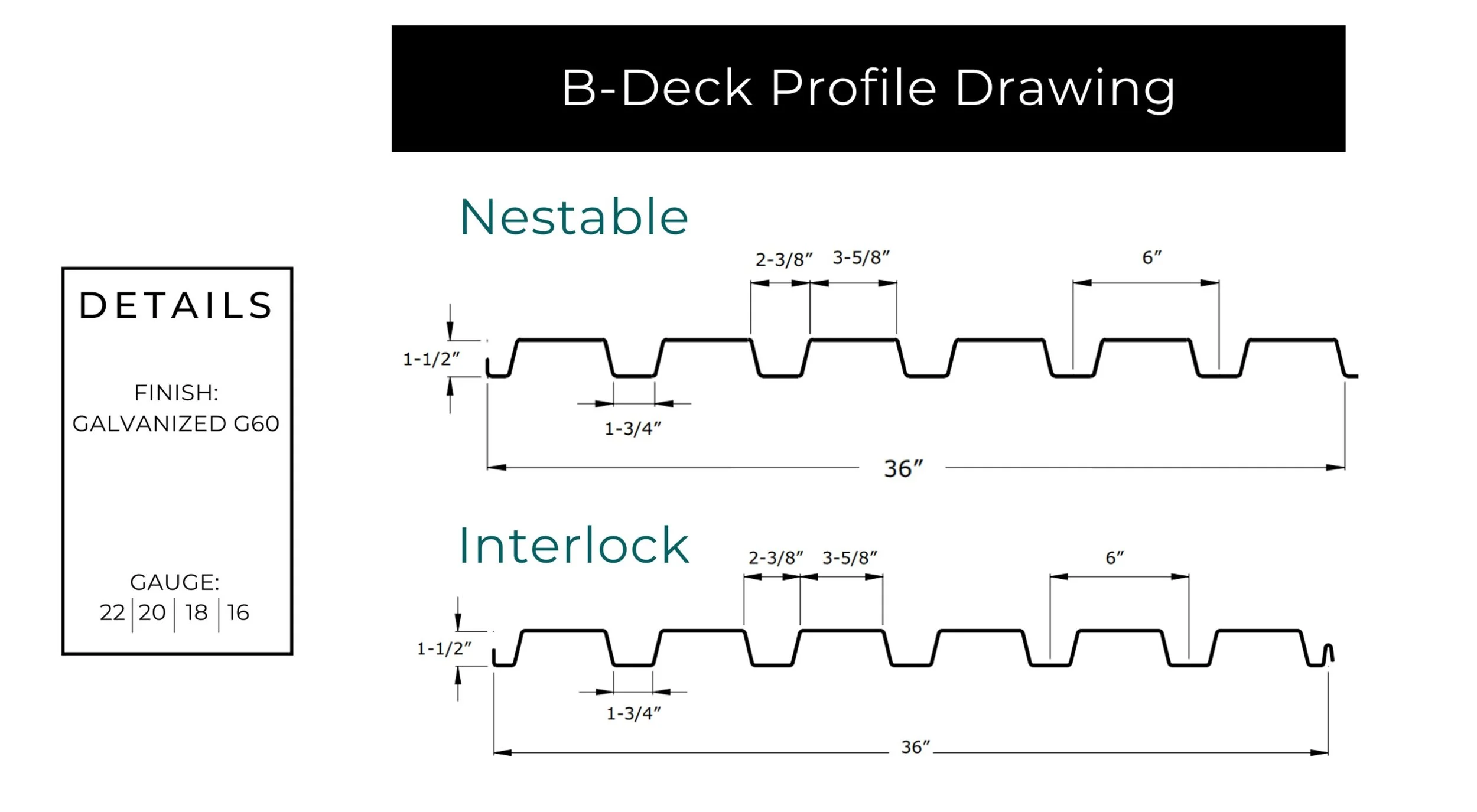
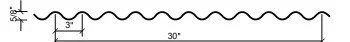
One of the most common decisions customers face is choosing between flat and striated standing seam panels. In this blog, we’ll break down the key differences, explore the impact of oil canning, and help you decide which finish is best suited for your project.
Flat Panels
Flat standing seam panels feature a smooth surface between seams, giving a clean, minimalist look that appeals to architects and modern designers.
Benefits of Flat Panels:
Modern Aesthetic: Clean lines and a crisp appearance ideal for contemporary designs.
Smooth Texture: Great for exterior walls or facades where texture is not desired.
Architectural Appeal: Flat panels often photograph well and are visually striking on commercial or residential builds.
Considerations:
Oil Canning Risk: Flat panels are more prone to a cosmetic phenomenon called oil canning, which causes visible waviness in the flat areas due to expansion and contraction of the metal.
Extra Precautions Needed: Installers may need to use thicker gauges or backer rods to minimize oil canning effects.
Striated Panels
Striated panels have shallow, continuous indentations (striations) running along the flat part of the panel. These are designed to add strength and reduce visual distortions.
Benefits of Striated Panels:
Reduced Oil Canning: The number one reason to choose striations — they help disguise or reduce the appearance of waviness.
Added Rigidity: The striations add minor structural strength to the panel without altering its basic look or performance.
Balanced Aesthetic: You still get a clean look, but with subtle texture that improves appearance over time.
Considerations:
Less Sleek Look: For designers seeking a glass-smooth facade, the texture may not be preferred.
Slight Shadowing: Depending on sunlight and roof orientation, striations may cast light shadows visible from certain angles.
When to Choose Which?
Choose Flat Panels if:
You prioritize a sleek, uninterrupted surface
The roof or wall is not in direct sunlight or highly visible
You’re using heavier gauge metal or taking other oil canning precautions
Choose Striated Panels if:
You want a more forgiving, uniform finish
The panels are wide or in lighter gauges
The surface will be visible under changing light conditions
What Is Oil Canning?
Oil canning is a cosmetic issue in metal panels where the flat areas appear wavy or distorted under certain lighting conditions. It’s not a structural defect, but it can affect the appearance of the roof or wall. This effect is more pronounced in flat panels, particularly those with large widths or thinner gauges.
While oil canning doesn’t impact the performance of the panel, it can detract from the visual appearance. Striated panels are one of the most effective ways to minimize this effect.